
To do that, we use the formula (P - AC)Q. Suppose we also want to find the monopolist's If allowed to decide herself, how much will this natural monopolistĪnd price, this natural monopolist will produce where MR = MC:įind price by plugging Q* into the demand equation: We'll calculate the values for P* and Q* below, and also explain the meaning of the shaded areas. In general then, for a natural monopoly, AC is said to decrease (as Q increases) through "some relevant range of market output". Remembering the relationship between marginal and average values, AC will be declining as long as MC is below it. Taking a closer look at these equations, you'll see that AC is always going to be greater than MC. The relative position of the AC and MC curves give the natural monopolist a cost advantage over its competition. The answer stems from the monopolist's natural (cost-related) barriers to entry. Your answer has been saved.Assume that a certain natural monopolist has the following demand and cost related curves: Total cost divided by the level of output Total cost less total fixed cost divided by the level of output Total fixed cost divided by the level of output The increase in total cost from producing one more unit Match the following cost definitions to their type. Total variable costs are $3200 and output is 200 and so variable cost per unit is $16. You seem to have done the calculation slightly wrong and have perhaps divided by 220 rather than an output of 200. Please select an answer No, that's not right. What is the variable cost per unit when they produce 200 units? When the firm produces zero output, the cost is $1000. When they increase output to 220, the cost rises to $4200. Total fixed costs are $1000 and output is 200 and so fixed cost per unit is $5.Ī firm produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. You seem to have done the calculation slightly wrong and are out by a multiple of 10.
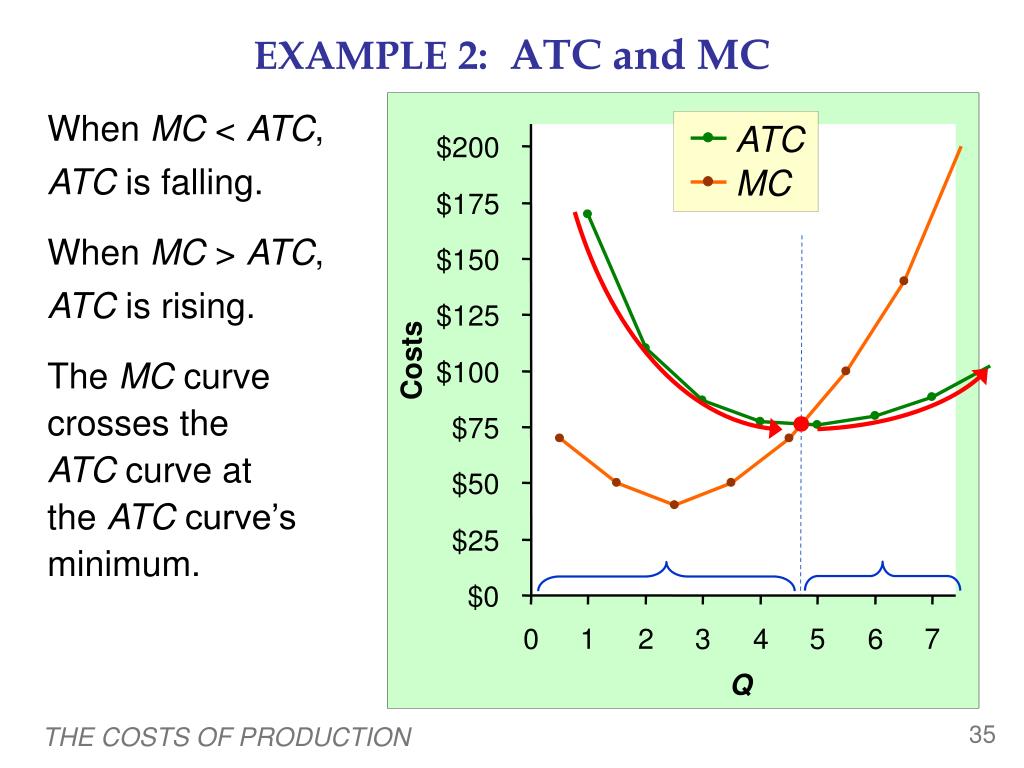
What is the fixed cost per unit when they produce 200 units? The marginal cost is falling and so the firm is facing diminishing returns to the variable factor.Ī firm produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. The firm is producing in the short run and so is not facing returns to scale. The firm is facing diminishing returns as the marginal cost is falling. Increasing returns to the variable factorĭiminishing returns to the variable factor When output rises to 240, the cost rises to $4100. Divide the total cost by the level of output and we get $19.10.Ī firm producing in the short run produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. Have you divided by 200 units rather than 220 units? Yes, that's correct. This is the total cost, you need to divide by the level of output to get average cost. What is the average cost of producing 220 units? Have you divided the increase in cost by the increase in output correctly?Ī firm produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. The marginal cost is the cost of one more unit (increase in cost of $200, from an increase in output of 20 equals $10 per unit). The marginal cost is the cost of one more unit. When output rises to 220, cost goes up by $200, but the marginal cost is the cost of one more unit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
